Morse Code

Morse code is a way to transmit messages over large distances using dots and dashes. Messages can be transmitted by radio or sent ship-to-ship with a light.
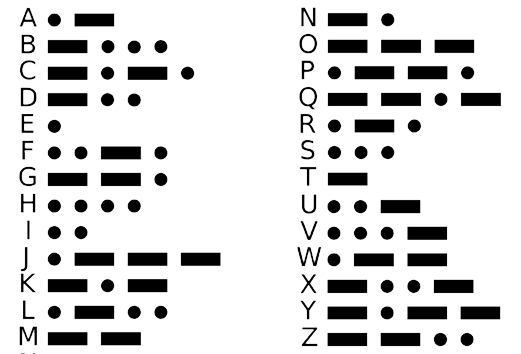
Timing is important in Morse code. Experts in Morse code follow these rules: A dash is 3 times longer than a dot. A space between letters is 3 times longer than a dot. A space between words is 7 times longer than a dot.
Notice that Morse code sends the most common letters using shorter sequences. So common letters, like E and T, are short while rare letters, like Q and Z, are long. This makes messages more efficient. One disadvantage to Morse code is that it needs to use spaces to separate words and letters. This makes Morse code less efficient. Today, we transmit messages using 1s and 0s. Using 1s and 0s, the most efficient code is Huffman code. Huffman code also sends the most common letters with shorter sequences, but it can do this without having to use spaces between words and letters, making it very efficient.
